Black eye – Symptoms, causes, and management
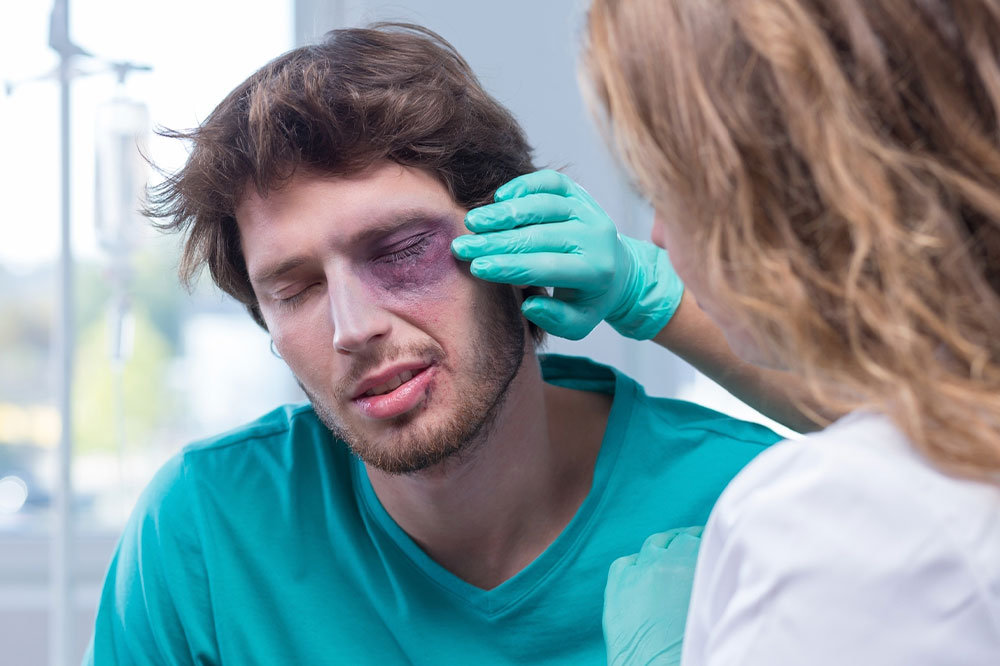
Black eye is a bruise on the eyelid skin caused by blunt trauma to the eye region. Sometimes, subconjunctival hemorrhage or broken blood vessels in the white of the eye can also be the reason for black eye. Like other bruises, it is nothing to worry about and will disappear in a week or two. But in some cases, the black eye is a warning sign of a more severe injury to the skull or the eye.
Symptoms and effects
Depending on the severity, the black eye can lead to several after-effects. But the area surrounding the injured eye will show discomfort, edema, and discoloration. Other symptoms associated with the black eye include abnormalities in the eyesight, headache, and soreness. The primary effects and outcomes of the black eye are:
Swelling: The affected area may be tender, puffy, and painful to the touch.
Discoloration: It is the most significant black eye symptom. Depending on the black eye’s severity, the discoloration may range from deep blue-black to light yellow.
Tenderness: The skin surrounding the affected eye may look tender and sore at the touch, especially when one exerts pressure.
Pain: It is the most common black eye symptom. The affected area is uncomfortable and sore, especially when moving the eye or surrounding facial muscles.
Vision changes: In some cases, the black eye is accompanied by vision changes like blurriness, double vision, and light sensitivity.
Causes
A blow to the head or face is one of the primary black eye causes. It ruptures the blood vessels under the skin, resulting in bruise formation. But there are several other causes of the black eye, ranging from ongoing prescribed treatments to medical conditions and underlying problems.
Some of the causes of the black eye are:
Medical conditions
Medical conditions like blood vessel diseases, bleeding disorders, and autoimmune conditions can amplify the risk of developing black eyes. These conditions weaken the blood vessels, making them susceptible to rupture and forming a bruise.
Physical trauma
Physical trauma to the head or face due to a fall, blow, or punch can be one of the causes of the black eye. Such injury ruptures the delicate vessels underneath the skin, resulting in discoloration and bruising around the eye.
Eye infections
Eye infections like styes or conjunctivitis can also lead to discoloration or swelling around the eye, mimicking black eye symptoms.
Blood thinners
Blood thinners also amplify a person’s risk of developing a black eye as they make the blood vessels fragile and susceptible to rupture when subjected to trauma.
Treatment
There is no magical treatment to get rid of the black eye overnight. However, some home remedies can accelerate the healing process. But it is a must to have a physician examine the eye before starting any treatment. Some of the best treatments for the black eye are:
Cold compress
Applying a cold object, a chilled spoon, or a bag of frozen peas to reduce the temperature in the area surrounding the eye immediately after an injury will help soothe the injury. Apply it for 15 to 20 minutes and repeat it as often as once every hour for the first 24 hours from the injury.
Warm compress
A day or two after applying the cold compress, one can switch to a warm compress. It accelerates the blood flow and allows healing.
Massage the area
Gently massage the region surrounding the bruise in the next few days. It helps activate the lymphatic system near the bruise and amplifies the healing process.
Snack on pineapple
Pineapples contain a mix of enzymes that lower inflammation and help heal.
Eat some Vitamin C
Vitamin C helps strengthen blood vessels and speed up recovery. Researchers suggest that vitamin C helps the blood clot, which helps reduce bruising and swelling.
Try bilberry extract
Like the cranberry and blueberry, bilberry extract has potent antioxidants that eliminate or reduce bruising by amplifying the Vitamin C effectiveness and strengthening the blood capillaries.
These are the basic remedies one can try to treat the black eye. However, if these remedies are ineffective in treating the black eye, the doctor may refer the patient to a specialist for further treatment. One may have to undergo surgery if there is a fracture in the skull.




